Category: Research Areas
-

Innate Immune Signaling Organelles Display Natural and Programmable Signaling Flexibility
The signaling organelles of the innate immune system consist of oligomeric protein complexes known as supramolecular organizing centers (SMOCs). Examples of SMOCs include myddosomes and inflammasomes, which respectively induce transcription-dependent and -independent inflammatory responses. The common use of oligomeric structures as signaling platforms suggests multifunctionality, but each SMOC has a singular biochemically defined function. Here,…
-

Inflammasomes within Hyperactive Murine Dendritic Cells Stimulate Long-Lived T Cell-Mediated Anti-tumor Immunity
Central to anti-tumor immunity are dendritic cells (DCs), which stimulate long-lived protective T cell responses. Recent studies have demonstrated that DCs can achieve a state of hyperactivation, which is associated with inflammasome activities within living cells. Herein, we report that hyperactive DCs have an enhanced ability to migrate to draining lymph nodes and stimulate potent…
-
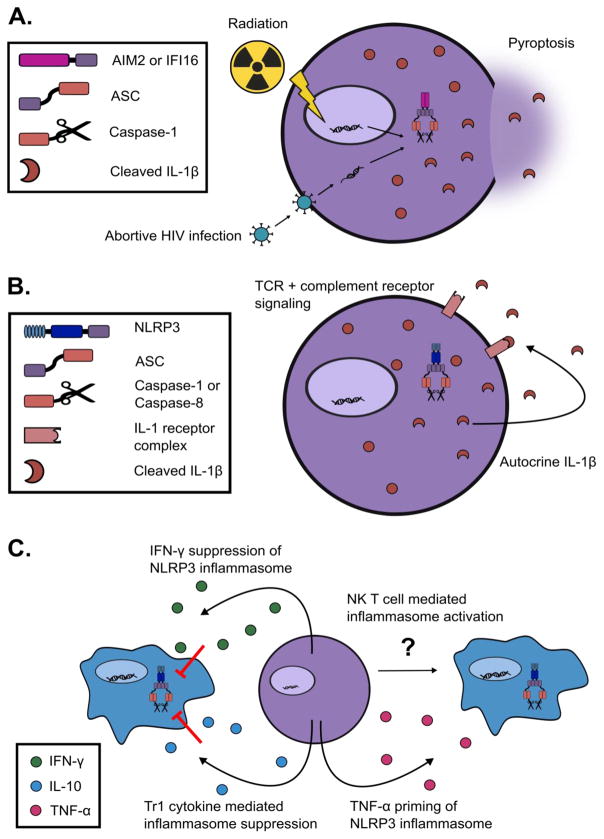
How Inflammasomes Inform Adaptive Immunity
An immune response consists of a finely orchestrated interplay between initial recognition of potential microbial threats by the innate immune system and subsequent licensed adaptive immune neutralization. The initial recognition integrates environmental cues derived from pathogen-associated molecular patterns and cell-intrinsic damage-associated molecular patterns to contextualize the insult and inform a tailored adaptive response via T…

